Biology MCQ Quiz - Objective Question with Answer for Biology - Download Free PDF
Last updated on Oct 21, 2024
Latest Biology MCQ Objective Questions
Biology Question 1:
Swine flu is caused by which virus?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 1 Detailed Solution
The correct answer is H1N1 virus.
 Key Points
Key Points
- A virus is the causative agent is responsible for spreading swine flu.
- Swine flu, also known as the H1N1 virus, is a relatively new strain of an influenza virus that causes symptoms similar to the regular flu.
- It originated in pigs but is spread primarily from person to person.
- Swine flu made headlines in 2009 when it was first discovered in humans and became a pandemic.
 Key Points
Key Points
- The flu, also called influenza, is a viral disease that affects the nose, throat, and lungs.
- Flu is caused by viruses that spread from one person to the other.
- It is spread through the cough or sneezes droplets from the infected person.
- It can also spread if a healthy person touches the objects containing the virus.
Biology Question 2:
A person with which blood group is called a 'public donor'?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 2 Detailed Solution
The correct answer is O
 Key Points
Key Points
Blood group:
- There are 4 main blood groups (types of blood) – A, B, AB and O.
- A person's blood group is determined by the genes we inherit from our parents.
- Each group can be either RhD positive or RhD negative, which means in total there are 8 blood groups.
Blood group O :
- This blood group has no antigen on an anti-A, B antibody so it can donate blood to any group.
- As it has no particular antigen present on it.
Thus, a person with 'O' blood group is called a universal donor.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
Blood group A:
- This blood group has A antigen on RBC and an anti-B antibody in plasma.
- So, it can donate only to the person with blood group A.
Blood group B:
- This blood group has B antigen on RBC and anti-A antibody in plasma.
- So, it can donate only to people with blood group B.
Blood group AB:
- This blood group has antigens A, B and it doesn’t have any antibodies that will fight blood groups.
- So, it can receive blood from any of the blood groups.
- It can donate blood only to AB blood groups.
Biology Question 3:
Where does the process of digestion of food begin in humans?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 3 Detailed Solution
The correct answer is Mouth

Key Points
The process starts from Buccal cavity or Mouth
Concept:
- Digestion:
- it is the complex process of turning the food we eat into nutrients, which the body uses for energy, growth and cell repair needed to survive.
- It also involves creating water to be excreted.
- Human Digestive system:
- Human Digestive system consists of the alimentary canal which can be further divided into various components. a) The buccal cavity b) food pipe or oesophagus c) stomach d) small intestine e) large intestine ending in the rectum f) the anus

- Mouth or Buccal cavity:
- Food is taken into the body through the mouth. The process of taking food into the body is called ingestion.
- our mouth has the salivary glands which secrete saliva.
- When we chew the food, saliva secreted from the salivary gland and mixes with food.
- Food becomes moisten by getting mixed with saliva.
- Partial digestion of food starts here.
- Food pipe:
- The swallowed food then passes into the food pipe or oesophagus.
- Food is pushed down by the movement of the wall of the food pipe.
- The stomach:
- The stomach is a thick-walled bag. Its shape is like a flattened U and it is the widest part of the alimentary canal.
- The inner lining of the stomach secretes mucous, hydrochloric acid, and digestive juices.
- The mucous protects the lining of the stomach.
- The acid kills many bacteria that enter along with the food and makes the medium in the stomach acidic, which helps digestive juices to break down the proteins into simpler substances.
- The Small Intestine:
- It is highly coiled and is about 6-8 meters long. It receives secretions from the liver and the pancreas.
- The digested food can now pass into the blood vessels in the wall of the intestine. This process is called absorption.
- The inner walls of the small intestine have thousands of finger-like outgrowths.
- These are called villi. (It increases the surface area of absorption of the digested food).
- Large intestine:
- It is wider and shorter than the small intestine.
- It is about 1.5 meters in length.
- Its function is to absorb water and some salts from the undigested food material.
Biology Question 4:
Which of the following vitamins is stored in the liver?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 4 Detailed Solution
The correct answer is All of these Key Points
Key Points
- The liver stores vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12:
- Vitamin A: The liver is the primary storage organ for vitamin A, which is fat soluble.
- Vitamin D: The liver can store vitamin D from the skin or diet.
- Vitamin K: The liver stores vitamin K, which is also stored in fat tissue. Vitamin K helps blood clot and is important for bone health.
- Vitamin B12: The liver stores vitamin B12.
- The liver is an organ in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen that performs many functions, including:
- Detoxifying metabolites
- Synthesizing proteins
- Secreting biochemicals for digestion and growth
- Regulating glycogen storage
- Decomposing red blood cells
- Producing hormones
- Secreting bile, which helps break down fat
- The body also stores excess fat-soluble vitamins in fat tissue.
- The body needs vitamins to function, grow, and develop, but it doesn't produce them itself.
- Vitamins must be acquired through food or supplements.
Biology Question 5:
For protection of plants and animal species and to provide for the prevention and control of water pollution, air pollution, and the environment, government of India has enacted several Acts. Which of the following combination of statements is correct?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 5 Detailed Solution
The Correct answer is Option 1.
 Key Points
Key Points
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974: This act was enacted to prevent and control water pollution and maintain or restore the wholesomeness of water.
- The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981: This act was enacted to prevent, control, and reduce air pollution in India.
- The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986: This act provides a framework for the protection and improvement of the environment and for matters connected therewith.
- The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972: This act was enacted to protect wildlife and their habitats in India.
- Hence Correct answer is Option 1.
Top Biology MCQ Objective Questions
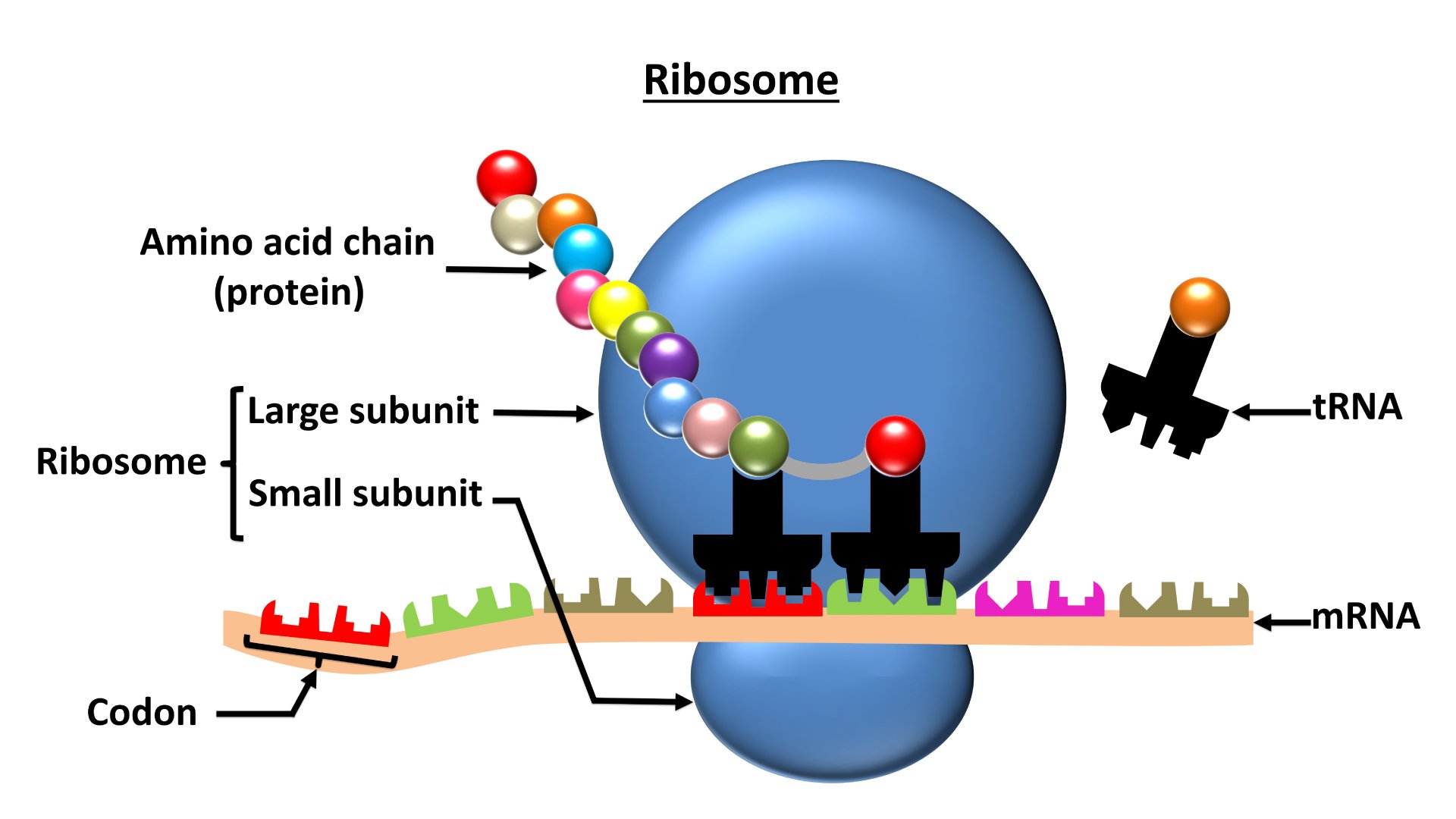
Ribosomes are sites for
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 6 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is Protein synthesis.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Ribosomes are membranous granular structures present in the cytoplasm.
- They were first observed under an electron microscope as dense particles by George Palade in the year 1953.
- Ribosomes are the site for ''protein synthesis'' so they are also called the ''protein factory'' of the cell.
- There are two types of ribosomes
- Eukaryotic ribosomes - 80s - occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell
- Prokaryotic ribosomes - 70s - occur in the cytoplasm as well as are associated with the cell membrane of prokaryotic cell.
- The subunits of the ribosomes are:
- 80s ribosomes - are made of 60s and 40s subunits.
- 70s ribosomes - are made of 50s and 30s subunits.
 Important Points
Important Points
- Composition of the structure of ribosome:
- They are composed of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and proteins
| Type | Composition |
| 70s | 60% rRNA + 40% proteins |
| 80s | 40% rRNA + 60% proteins |
 Additional Information
Additional Information
- Photosynthesis: It is the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize nutrients from carbon dioxide and water. In this process, plant the chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and release oxygen.
- Synthesis of Fatty acids occurs in the cytoplasm.
Among the following statements which is/are correct?
1. Plants convert energy from sunlight into food stored as carbohydrates
2. Plants have chlorophyll
3. Plant cells do not have cell walls
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 7 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFConcept:
Photosynthesis:
- The leaves have a green pigment called chlorophyll.
- It helps leaves to capture the energy of the sunlight.
- This energy is used to synthesise (prepare) food from carbon dioxide and water. Since the synthesis of food occurs in the presence of sunlight, it is called photosynthesis.
In the presence of sunlight Carbon dioxide + water → Carbohydrate + oxygen.
- Some plants, green algae, and cyanobacteria can perform photosynthesis.
- The process of photosynthesis is commonly written as
6CO2 + 6H2O + Sun-Light → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Plant cells have a cell wall to protect them and make them rigid structure.
Explanation:
1. Plants convert energy from sunlight into food stored as carbohydrate’s - Correct
2. Plants have chlorophyll. - Correct
3. Plant cells do not have cell walls. - Incorrect.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
In the plant cells, there are different components and organelles for specific functions-

- Cell Wall – It is a rigid layer composed of cellulose. It is the outermost layer of the cell, below this cell membrane is present. The primary function of the cell wall is to protect and provide structural support to the cell.
- Cell Membrane – It is a semi-permeable membrane that helps in regulating and the substance for entry and exit inside and outside the cell.
- Nucleus – It is a vital part of the cell as it contains all the information or DNA of the cell and their heredity information for growth and cell division.
- Vacuole – Most of the part of the plant cell is occupied by the vacuole. It is surrounded by Tonoplast. The vital role of the vacuole is to provide support again the pressure of the cell wall.
- Golgi apparatus – They act as a transport system in the cell, as they transport various molecules to a different part of the cell.
- Ribosomes – They are the sites of protein synthesis, also termed as the protein factory of the cell.
- Mitochondrion – They break the complex molecules and produce energy and hence called the powerhouse of the cell.
- Lysosomes – They are termed suicidal bags as they hold the enzymes that are capable to digest the whole cell itself.
Which juice secreted by the organs in the alimentary canal plays an important role in the digestion of fats?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 8 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is Bile juice, Pancreatic juice.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Bile juice, Pancreatic juice secreted by the organs plays an important role in the digestion of fats.
- Bile juice is secreted by the liver.
- It does not contain any types of enzymes.
- The bile juice helps to make the food alkaline and break down the fat molecules.
- Pancreatic juice is secreted by the pancreas.
- It contains enzymes like amylase, trypsin, pancreatic lipase, nucleases, amylase, and lipase.
- Secretion of the Pancreatic juice is regulated by the hormones secretin and cholecystokinin.
- Lipase is the digestive enzyme of fat.
- Ptyalin is the digestive enzyme of the Saliva.
- Hydrochloric acid is produced naturally in the human stomach to help the digestion of food.
Which of the following organism breathes from skin?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 9 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFWhich of the following aquatic animals does NOT have gills?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 10 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is Whale.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Gills are respiratory organs found in most aquatic organisms.
- Gills can extract dissolved oxygen from water and excrete carbon dioxide.
- Gills can be found in Octopus, Squid, Clownfish, Tadpole, Prawn, etc.
- Lungs are the breathing organ of Whales.
 Additional InformationRespiratory organs of different Animals:
Additional InformationRespiratory organs of different Animals:
| Animal | Respiratory Organ |
|---|---|
| Earthworm | Skin. |
| Whale | Lungs |
| Spider, Scorpion | Booklungs. |
| Cockroach | Trachea. |
| Tadpole, Fish, Prawn | Gills |
| Frog | Skin, Lungs, Buccal cavity |
| Amphibians, mammals, and birds | Lungs. |
Which of the following organelles shows similarity to a prokaryotic cell?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 11 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is Both chloroplast and mitochondria
Concept:
Theory of endosymbiosis:-
- Symbiotic relationship, where one organism lives inside the other, is known as endosymbiosis.
- The theory proposed that mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved from engulfed prokaryotes.
- A large anaerobic bacteria engulfed an aerobic prokaryote, which then formed an endosymbiotic relationship with the host, gradually developing into a mitochondrion.
- It is believed that chloroplasts originated from a cyanobacterial endosymbiont.

Explanation:
Similarities between Prokaryotic cells, Mitochondria, and Chloroplast:
- Mitochondria and chloroplast are of the same size as prokaryotic cells.
- Mitochondria and prokaryotic cells both have their own circular DNA.
- The ribosome of bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have a 70S type of ribosome.
- Divides by binary fission.
| Characters | Prokaryotic cell | Mitochondria | Chloroplast |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Extra Circular DNA |
present | present | present |
|
Ribosomes |
70s | 70s | 70s |
| Replication | Binary fission | Binary fission | Binary fission |
| Size | 1 to 10 micrometre | 1 to 10 micrometre | 1 to 10 micrometre |
| Appearance on earth | about 1.5 billion years ago | about 1.5 billion years ago | about 1.5 billion years ago |
| Electron transport system | Found in the plasma membrane of the cell | Found in the plasma membrane of mitochondria | Found in the plasma membrane of Chloroplast |
Which of the following helps in the blood clotting?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 12 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDF- Vitamin K is a vitamin found in leafy green vegetables, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts.
- In the body, vitamin K plays a major role in blood clotting. So it is used to reverse the effects of “blood-thinning” medications when too much is given; to prevent clotting problems in newborns who don’t have enough vitamin K, and to treat bleeding caused by medications.
Tricks:
What is the cell wall of a plant made of ?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 13 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is Cellulose.
- Plant cell walls are primarily made of cellulose.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Cellulose is the most abundant macromolecule on Earth.
- Cellulose fibers are long, linear polymers of hundreds of glucose molecules.
- These fibres aggregate into bundles of about 40, which are called microfibrils.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
- Carbohydrates are the sugars, starches, and fibres found in fruits, grains, vegetables, and milk products.
- A carbohydrate is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms.
- Lipids are molecules that contain hydrocarbons and make up the building blocks of the structure and function of living cells.
- A lipid is a biomolecule that is soluble in nonpolar solvents.
- A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid also known as fat molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids.
- It consists of a Triglyceride and Cholesterol centre, surrounded by a phospholipid outer shell, with the hydrophilic portions oriented outward towards the surrounding water and lipophilic portions oriented inward toward the lipid centre.
Influenza disease is caused by which of the following?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 14 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFInfluenza disease is caused by a Virus.
|
Diseases |
Caused By |
|
Tuberculosis |
Bacteria |
|
Influenza |
Virus |
|
Fungal Infection |
Fungi |
|
Malaria |
Protozoan |
Trick: Virus influence many Diseases
In which stage of meiosis does synapsis take place?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Biology Question 15 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFConcept:
- The cell is the basic unit of life. Life arises from pre-existing cells. Cells grow and multiply to form a diversity of life forms, this process of growth and multiplication of cells is called Cell Division.
- Cell division is of three types:
- Mitosis - Equational division, occurs in somatic (non-sex) cells
- Meiosis - Reducttional division, occurs in sex cells
- Amitosis - Direct type of division, occurs in prokaryotes
- Meiosis can be further divided into two stages - Meiosis I and Meiosis II
Explanation:
- Prophase I of Meiosis I has 5 sub-stages
- Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene, Diakinesis.
- The Zygotene stage is characterized by the pairing of homologous chromosomes called the ''Synapsis''
- The pairs of homologous chromosomes are called Bivalents.
- There develops a structure between the homologous chromosomes called the synaptonemal complex. It is a tripartite structure i.e. it is made up of 3 thick lines of DNA and protein.

 Additional Information
Additional Information
- Leptotene: During leptotene, the chromatin condenses to form the chromosomes. Chromosomes are the longest and thinnest in this stage.
- Pachytene: This stage is characterized by the occurrence of crossing over. Non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes exchange their genetic parts.
- Metaphase I: The first metaphase of meiosis characterized by the alignment of paired chromosomes along the center (metaphase plate) of a cell, which ensures that two complete copies of chromosomes are present in the resulting two daughter cells of meiosis I.


